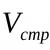What percentage of the salary is the advance? Dependence of advance payment on salary Rules for calculating advance payment and salary

At the beginning of 2018, there are no fundamental changes in terms of calculating the amount of the deposit, so it is determined according to the previous 2017 scheme: in proportion to the employee’s actual time worked.
Payment of monthly earnings in advance is permitted by Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and consists of transferring money for the half of the month worked to the employee. The rest is paid after the second half of the month. Thus, the legislator insists on settlement between the employer and the subordinate at least twice a month.
Advance payment is what percentage of the salary according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2018?
The Labor Code, in this regard, does not establish any specific interest rates. It only indicates that the employee must pay his salary at least twice a month. And the size of the wage advance according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2018 is determined based on the specific situation.
The advance, in this case, will be 50% of the total amount of income, but taking into account the deduction of tax 13% / 2 (two halves of the month) = 7.5% (for one half). So, the percentage of the advance payment is 42.5% (50% - 7.5%).
But a certain amount of interest is not specified either in the employment contract or in the local regulations of the organization where the person works; only the frequency of payments for work is established.
Advance payment of wages according to new rules in 2018
In 2017, changes were made by the Federal Law to labor legislation: the procedure and timing for calculating advance payments to working citizens was adjusted. Now an employee of the company must receive remuneration for work at least twice per month, with every 15th working day being the day of payment of the advance, but it can be established earlier, at the discretion of the employer.
By the way, what deductions from wages are under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is described.
How much is the salary advance paid in 2018?
The burning question of what percentage of the advance payment of salary is of concern to all workers in 2018. It is calculated in proportion to the period worked. If the entire income for 30 days is 100,000 rubles, then by the 15th day the advance will be equal to 50,000 rubles, but this does not take into account income tax (13%).
With personal income tax, the amount will be calculated as follows:
- 100 000 – 13 % = 87 000;
- 87 000/ 2 = 43 500.
The advance payment for 15 days will be 43,500 rubles.

New terms for payment of advance payments and salaries in 2018
New deadlines have indeed appeared. This is every 15 days. The manager can set the day of payment of half the salary on any day of the month, the main thing is that the interval between the first part and the second does not exceed 15 days.
If the day of advance payments is a day off, then the money must be issued on the first working day before them. So, the scope of remuneration for employees is established by the legislator, and the specific number is chosen by the employer.
Do I need to pay personal income tax on advance wages?
Personal income tax is charged on the total amount earned by the employee for a monthly period. It is set at 13% and has not changed so far. Profit tax is not withheld from the advance payment, but personal income tax is reflected on its amount, since advance deductions are formed taking into account the final amount of a person’s income, which remains after deducting 13 percent tax.
Application for advance payment of wages - sample
Description of the sample application:
- typewritten or handwritten text on a white sheet of paper;
- on the right, starting from the center of the sheet - the addressee (includes the name of the place of work, full name of the boss, address) and the applicant (name, address);
- below - in the center: the word “STATEMENT”;
- with a paragraph indentation is the substantive part, it can be formulated in any way, it is only important that it is clear what the applicant wants and in what amount;
- it is recommended to indicate the reasons for the application, as they help convince the manager of the need to establish an advance payment procedure in relation to the employee;
- At the end, a signature is affixed with a transcript and date.
Order for payment of advance from wages - sample
All organizational issues at the enterprise are resolved in the form of orders issued by the person heading it. So, in order to establish an advance payment procedure for subordinates for work, the employer creates an order about this.
It is drawn up according to the rules for the preparation of local acts established in the organization, taking into account the generally accepted rules of office work and the preparation of documents. He must also go through an approval procedure with certain authorized employees of the company.
Thus, remuneration in the form of advance payments has many nuances and requires good regulatory awareness of the management team in this matter.
1. How often and within what time frames must wages be paid to employees?
2. How to determine the amount of advance payment due to employees.
3. In what order are insurance premiums and personal income tax from wages and advance payments calculated and paid?
“The main thing in settlements with employees regarding wages is to correctly calculate the amounts due to them.” This statement is only half true: it is important not only to correctly calculate employee salaries, but also to pay them correctly. At the same time, the stumbling block for many is paying advances to employees. Is it necessary to split the salary into an advance payment and a final payment if the amount is already small? Is an advance paid to external part-time workers? How to calculate the advance amount? We will look into these and other issues related to the payment of wages to employees in this article.
Frequency of salary payment
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the employer’s obligation to pay wages to employees at least every half month(Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It should be noted that the Labor Code does not contain such a thing as an “advance” at all: according to its wording, this is wages for the first half of the month. And the widely used concept of “advance” came from a Soviet-era document, Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers dated May 23, 1957 No. 566 “On the procedure for paying wages to workers for the first half of the month,” which is still in effect to the extent that does not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, to make it easier to understand, in this article, advance means wages for the first half of the month.
So, for wages, the frequency of payment is established at least every half month. At the same time, other payments to employees have their own deadlines:
- vacation pay must be paid no later than 3 days before the start of the vacation;
- Severance pay must be paid on the day the employee leaves.
But the payment of sick leave is precisely tied to the payment of wages: benefits must be paid on the day closest to the date of payment of wages after the award of benefits. If such the nearest day is the day of payment of the advance, then the benefits must be paid along with it.
! Note: The requirement of the Labor Code to pay wages at least twice a month does not contain any exceptions and is mandatory for all employers to fulfill in relation to all employees (Rostrud Letter No. 3528-6-1 dated November 30, 2009). That is advance must be paid
- , including:
- if the employee is an external part-time worker;
- if local regulations of the employer, employment contracts, etc. Payment of wages is established once a month. This provision is void and cannot be enforced, as it violates the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- regardless of the amount of earnings and the accepted wage system.
If the employer nevertheless neglected the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to pay wages to employees at least every half month, then in the event of an inspection by the labor inspectorate he faces liability in the form of a fine(Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for officials – from 1,000 rubles. up to 5,000 rub.
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 1,000 rubles. up to 5,000 rub.
- for legal entities – from 30,000 rubles. up to 50,000 rub.
Deadlines for payment of wages
Currently, labor legislation does not contain specific terms for payment of wages, that is, the employer has the right to set them independently, enshrining them in the internal labor regulations, collective agreement, and employment contracts with employees (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The following must be taken into account:
- The time interval between salary payments should not exceed half a month. In this case, payments do not necessarily have to fall within one calendar month (Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242). For example, if wages for the first half of the month are paid on the 15th day, then for the second - on the 30th (31st) of the current month, if for the first - on the 25th, then for the second - on the 10th of the next month, etc. . In addition, the employer can set the frequency of payment of wages more often than once every half month, for example, every week - this approach is acceptable since it does not worsen the situation of employees and does not contradict the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Deadlines for payment of wages must be indicated in the form of specific days, and not time periods (Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242). For example: 10th and 25th of every month. A wording such as “from the 10th to the 13th and from the 25th to the 28th” is unacceptable, since in fact the requirement of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to pay wages at least every half month may be violated: the employee will receive a salary on the 10th, and the next payment will be on the 28th, that is, the gap between payments will exceed half a month.
- If the established payment day falls on a weekend or non-working holiday, then wages must be paid on the eve of this day (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
! The employer bears (including advance payments and other payments in favor of employees): financial, administrative, and in some cases even criminal.
Advance amount
The Labor Code does not contain requirements regarding the proportions (amounts) in which parts of wages should be paid. However, Decree No. 566, which was already mentioned above, provides that the amount of the advance must not be lower than the worker’s tariff rate for the time worked. Despite the fact that this resolution deals with the wages of workers, a similar approach can be used in relation to other workers.
The amount of advance payment to be paid to the employee can be calculated in one of the following ways:
- in proportion to the time worked;
- in the form of a fixed amount, for example, calculated as a percentage of the salary.
Using the second option, paying an advance in a fixed amount, has one significant drawback - the likelihood that the employee will not work off the advance received. For example, in cases where an employee was on sick leave for most of the month, on leave without pay, etc. and was paid an advance, at the end of the month the accrued wages may not be enough to cover the advance payment. In this case, the employee has a situation, the retention of which is associated with certain difficulties for the employer.
Using the first option, paying an advance in proportion to the time actually worked, is more preferable, although more labor-intensive for the accountant. In this case, the amount of the advance is calculated based on the employee’s salary and the days he actually worked for the first half of the month (based on the time sheet), so the possibility of “transferring” the advance is practically excluded. Rostrud specialists in Letter No. 1557-6 dated 09/08/2006 also recommended that when determining the amount of the advance, take into account the time actually worked by the employee (actually completed work).
! The Labor Code obliges the employer for each payment of wages (including advance payments) notify the employee in writing(Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- on the components of wages due to him for the relevant period;
- on the amount of other amounts accrued to the employee, including monetary compensation for the employer’s violation of the established deadline for payment of wages, vacation pay, dismissal payments and (or) other payments due to the employee;
- about the amounts and grounds for deductions made;
- about the total amount of money to be paid.
The specified information is contained in the pay slip, the form of which is approved by the employer himself, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
Methods of payment of wages
Wages are paid to employees either in cash from the employer's cash desk or by bank transfer. In addition, labor legislation does not prohibit part of wages (no more than 20%) from being paid in kind, for example, in finished products (Part 2 of Article 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the specific method of payment of wages must be specified in the employment contract with the employee. Let us dwell in more detail on monetary forms of payment of wages.
- Payment of wages in cash
Payment of wages to employees from the cash register is documented with the following documents:
- payment (form T-53) or payroll (form T-49);
- expense cash order (KO-2).
If the number of employees is small, then the payment of wages to each employee can be processed using a separate cash order. However, with a large staff, it is more convenient to draw up a payroll (settlement and payment) statement for all employees and make one expense order for the entire amount paid according to the statement.
- Transfer of salary to a bank card
The conditions for paying wages in non-cash form must be specified in the collective agreement or employment contract with the employee. For the convenience of transferring wages, many employers enter into appropriate agreements with banks for the issuance and servicing of salary cards for employees. This allows the entire amount of wages to be transferred in one payment order with a register attached, which specifies the amounts to be credited to the card account of each employee.
! It is possible to transfer wages in non-cash form only with the consent of the employee and only using the details specified in his application. In addition, the employer cannot “bind” its employees to a specific bank: labor legislation gives the employee the right at any time to change the bank to which his wages should be transferred. In this case, it is enough for the employee to notify the employer in writing about the change in payment details for payment of wages no later than five working days before the day of payment of wages (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for calculating and paying personal income tax and insurance contributions from wages
We found that employees must be paid at least twice a month. In this regard, many people have a question: is it necessary to calculate insurance premiums and personal income tax from the advance payment? Let's figure it out. According to the law, insurance premiums must be calculated based on the results of the month for which wages are accrued (Clause 3, Article 15 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ). As for personal income tax, in accordance with the Tax Code, the date of receipt of income in the form of wages is recognized as the last day of the month for which income was accrued for work duties performed (clause 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, Neither insurance premiums nor personal income tax need to be charged on the advance payment.
The deadlines for payment of insurance contributions from wages are the same for all employers and do not depend on the date of payment of wages. Currently, contributions to extra-budgetary funds must be paid before the 15th day of the month following the month of salary calculation (clause 5 of Article 15 of Law No. 212-FZ). An exception is insurance contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation against accidents and occupational diseases - they must be paid on the day established for receiving funds from the bank to pay wages for the past month (clause 4 of Article 22 of Law No. 125-FZ).
Unlike insurance premiums, the deadline for paying personal income tax depends on the date and method of payment of wages:
Payroll accounting
In accounting, the calculation of wages, as well as personal income tax and insurance contributions, is reflected on the last day of the month worked. In this case, the following entries are made:
|
date |
Account debit | Account credit | |
| Date set for payment of wages for the first half of the month | 70 | 50(51) | Salaries for the first half of the month were paid from the cash register (transferred to employee cards) |
| Last day of the month | 20(23, 26, 44) | 70 | Salary accrued |
| Last day of the month | 70 | 68 | Personal income tax withheld from wages |
| Last day of the month | 20(23, 26, 44) | 69 | Insurance premiums calculated from wages |
| Date set for payment of wages for the second half of the month (final payment) | 70 | 50(51) | Salaries paid from the cash register (transferred to employee cards) |
| The last day of the deadline established for the payment of wages according to the statement from the cash register | 70 | 76 | Amount of uncollected salary deposited |
| The next day after the end of the period established for payment of wages according to the statement from the cash register | 51 | 50 | The deposited salary amount is credited to the current account |
| 50 | 51 | Received money from the current account for the issuance of deposited salaries | |
| When an employee applies for wages not received on time | 76 | 50 | Deposited wages issued |
Do you find the article useful and interesting? share with colleagues on social networks!
There are still questions - ask them in the comments to the article!
Yandex_partner_id = 143121; yandex_site_bg_color = "FFFFFF"; yandex_stat_id = 2; yandex_ad_format = "direct"; yandex_font_size = 1; yandex_direct_type = "vertical"; yandex_direct_border_type = "block"; yandex_direct_limit = 2; yandex_direct_title_font_size = 3; yandex_direct_links_underline = false; yandex_direct_border_color = "CCCCCC"; yandex_direct_title_color = "000080"; yandex_direct_url_color = "000000"; yandex_direct_text_color = "000000"; yandex_direct_hover_color = "000000"; yandex_direct_favicon = true; yandex_no_sitelinks = true; document.write(" ");
Normative base
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations and Instructions for its application”
- Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers of May 23, 1957 No. 566 “On the procedure for paying wages to workers for the first half of the month”
- Letter of Rostrud dated November 30, 2009 No. 3528-6-1
- Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242
Find out how to read the official texts of these documents in the section
They call it an advance part of accrued salary employees of enterprises and institutions for the performance of their labor duties. The date of issuance of the advance must be written in the collective or labor agreement.
Any enterprise is obliged to give an advance in the 1st half of the month. Salaries must be paid to the worker once every six months on a day determined by the organization, corporate contract, or contract with the employee. As required by law (Part 6 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), any entrepreneur is obliged to divide his salary into 2 parts.
According to Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2018, payment is made once every half month. This is confirmed by contracts with employees (corporate or labor). The employer is obliged to make payments 2 times a month, as stated in Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The payment in total cannot be less than the accrual for the first half of the month.
This provision for payment of wages 2 times a month should be in the contract for any form of payment. When a person gets a job, he must be given to read the documents of the enterprise and the contract, which indicates the days for issuing the advance. The legal requirements apply to all entrepreneurs without exception, including private entrepreneurs with employees. For all participants in an organization or enterprise, employee salaries should be the most important thing.
The amount is 1/300 of the refinancing rate accrued for any day of delay. For the calculation, the price in effect on the date of the transaction is taken. Payment is made by the employer according to terms without agreement. Payment days are confirmed in the collective agreement and in the order. Employees should check these documents to clearly know the payment dates. Nobody can stop them from doing this. A document on payment terms is submitted to the bank once a year.
How to calculate correctly
Various methods are used to calculate the advance. The use of calculation based on time worked can only be confirmed in the organization’s salary rules. This method is the main one.
If the calculation is applied as a percentage of salary, the amount does not change for working days. Usually - 50% of salary.
Example 1: The employee works as a storekeeper for the company. Salary - 35,000 rubles. The company document indicates the percentage of salary for the advance - 50%. The employee must receive an advance payment for half a month worked:
35,000 * 50% = 17,500 rub.
When deciding on the size of this percentage of earnings, you need to take into account some other reasons:
- work situation and difficulties;
- qualifications;
- the success of the employee;
- working at several jobs.
Example 2: employee income - 68,000 rubles. Personal income tax – 8840 rub. (68,000 * 13% / 100%). The accrual date is the 15th. Consequently, for August 2018 they are required to pay an advance on 08/15/2018 in the amount of 26,891 rubles.
((68,000 – 8840) / 22 * 10) = 26,891 rubles, where
10 days - These are days worked for half a month; there are 22 working days in a month.
The advance is set at 50% of the monthly earnings, excluding personal income tax.
Employees have the right to check the calculation of their advance payment in the accounting department based on the submitted documents. If inaccuracies and discrepancies are found, the employee may request correction of errors and recalculation of the advance payment.
Payment methods
- The days of payment of salaries in cash are confirmed by the organization. Usually from 3 to 5 days, after the amount is deposited. Payments more than 2 times a month are not prohibited. To prove legality, salary payment days are confirmed in the company’s documents. Cash is paid through the cash register.
- Cashless payment means transferring the amount to a bank card. A non-resident employee is paid only in this form. This is the most promising type of payment and the safest, allowing you to save significant money on maintenance.
- Delivery in kind. Special payment processing is done in a convenient form. The payroll form T-53 is mainly used.
Accrual period
Rostrud civil servants advise issuing an advance on the 15th or 16th. Firms can make payments on the 25th, but when hiring an employee at the beginning of the month, this may happen. payment delay for 15 days or more. Then workers can go to court and stop working
The dates for payment of earnings and advance payments are set by the employer independently, without the participation of government agencies. If the date changes, amendments must be made to the collective agreement, as well as to employee contracts.
Since November 19, 2010, a standard has been in force according to which wages are paid within 7 calendar days after the month of accrual.
 Time between payments should not be more than 16 calendar days. The main thing is that employees control the delivery deadlines, which in real life are often missed for various reasons, and only the employees themselves can punish the entrepreneur for this, which they are not always ready to do.
Time between payments should not be more than 16 calendar days. The main thing is that employees control the delivery deadlines, which in real life are often missed for various reasons, and only the employees themselves can punish the entrepreneur for this, which they are not always ready to do.
Salaries are paid only on working days. If the established payment date falls on a weekend or holiday, the payment is made in advance.
Responsibility for possible violations
For the delay in issuing advance payments to tenants under Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation, 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation impose fines:
- For the head of an enterprise, entrepreneur: 1000 – 5000 rubles.
- For an enterprise – 30,000-50,000 rubles. When recruiting again - up to 70,000 rubles.
Additional information is presented in the video.
Every work activity involves performing work for remuneration. Labor Code of the Russian Federation, namely stat. 136, obliges employers to pay off obligations with employees at least 2 times a month. How is the advance calculated and what percentage of the 2016 salary is it? What are the legal deadlines for payments? We will look at what internal documents to document all operations in this section. The current changes are listed below, along with possible penalties for those responsible in case of violation of workers' rights.
The Labor Code clearly states that wages must be paid to employees every half month, that is, twice a month. The periods cannot exceed 15 days; transfers are often not prohibited. Specific payment terms before October 3 were not indicated anywhere, and the employer set them independently in internal rules, employment contracts or a collective agreement. It turns out that the advance is earnings for the first half of the month.
Explanations from regulatory authorities:
- Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 22-2-709 dated February 25. 2009 - the calculation of the advance and salary should be such that the result is approximately equal amounts.
- Letter of the Federal Labor Service No. 1557-6 dated September 8. 2006 – advance payments should be made for actual hours worked.
- Oral consultations with Rostrud - advance payments are recommended to be made in the middle of the month, that is, on the 15th/16th. The amounts to be paid should not be less than what the employee actually earned during the period at the established tariff rate/salary.
These explanations from officials are not binding, but the opinions presented must be taken into account. Having determined what percentage of the salary the advance is, it is necessary to fix the size and terms in the internal documents of the organization, as well as employment contracts. The calculation includes the amounts of additional payments and allowances for combinations, including external ones; processing; replacing other employees; other. Bonuses, financial assistance, benefits and social payments are not included.
Important! From October 3, 2016, by Law No. 272-FZ of June 3. 2016 established that salaries cannot be paid later than 15 calendar days from the end of the period for which the remuneration was accrued (stat. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If necessary, the employer is obliged to set new payment terms.
The amount of the advance can be determined in different ways. The first takes into account weekends/holidays when calculating, the second does not, which is more profitable if there are a large number of holidays in the period. The selected calculation algorithm should be specified in the wage regulations at the enterprise. Let's look at both methods using a specific example.
Employee Igor Viktorovich Gvozdenko works at Spetsstroy LLC as a civil engineer. His salary is 46,000 rubles, the bonus based on length of service is 4,000. Let’s calculate the amount of the advance and salary for September, the period has been fully worked out. We take into account what percentage of the salary is set for the advance payment in the organization.
The first method uses the Formula: (Salary + Allowances) x 50% = 25,000 rubles.
The second method - holidays and weekends are taken into account, the calculation is based on the actual time worked. Let’s change the conditions of the example and determine the advance/salary for May 2016. There are a total of 19 working days in the month, of which 7 days in the first half.
Formula for calculation: (Salary + Allowances) x Number of days worked for 1 half / Number of days worked in total = 18,421 rubles. The result was much lower than in method 1.
The rest of the earnings will be issued “in hand” according to the deadline for payment of wages. All taxes and contributions required by law are calculated based on the results of the whole month and transferred to the budget by the employer.
Responsibility of the employer for delays in payment of wages:
- For organizations - a fine of 30,000-50,000 rubles is charged, and in case of repeated violation - 50,000-100,000 rubles.
- For responsible persons (manager, owner of the organization), a fine of 10,000-20,000 rubles is charged, and in case of repeated violation, they face disqualification for 1-3 years or a fine of 20,000-30,000 rubles.
- For each day of delay, the employer is obliged to pay penalties to employees in the amount of at least 1/150 of the current refinancing rate (from 10/03/16).
The employer's liability for failure to pay an advance in the established percentage of the salary:
- For organizations - a fine of 30,000-50,000 rubles, repeated violation - a fine of 50,000-70,000 rubles.
- For individual entrepreneurs – 1,000-5,000 rubles, repeated violation – 10,000-30,000 rubles.
- For responsible persons - 1,000-5,000, repeated violation - disqualification for a period of 1-3 years or a fine of 10,000-20,000 rubles.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
The correctness of the preparation of financial statements depends on the correctness and timeliness of accrual, registration and payment of salary advances. In order to avoid administrative fines for incorrectly or lately paid salary advances, study this article, which provides the most up-to-date information on this issue for 2019.
When carrying out work, a person wants the result to be paid well and on time. But ignorance of the basic rules by which the calculation, payment, and withholding of taxes on wages and advances occurs often becomes a reason for the employer to delay making a transfer to his employee or not to make it at all. This article will tell you about the rules for paying advances and salaries, what percentage of the salary is an advance, liability for violating these rules, and how to correctly file and withhold taxes on salaries and advances.

How are salaries and advances paid?
It’s worth starting with the fact that such a concept as an “advance” in relation to wages does not exist in the 2019 legislation.
Based on the norms of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), in 2019, wages must be paid at least once every half month.
This payment occurs on the day established by contracts with employees (collective or labor), internal labor regulations, for example, the 15th of each month.
Thus it turns out that An advance is the first part of the salary payment for a certain period. Although the specific period for making such payments is not fixed by law, regulatory authorities have provided some clarification.
The letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709 states that when calculating an advance for each half of the month, the amount should be approximately equal. If we turn to another letter written by the Federal Service for Labor and Employment on September 8, 2006 No. 1557-6, which states that when determining the amount of the advance, one should take into account the time that the employee actually worked, the corresponding conclusion follows: In order to receive two approximately equal amounts for the time actually worked in a specific period, the first payment should be made approximately in the middle of a specific working period.
This conclusion is confirmed by oral consultations with Rostrud employees, who recommend paying the advance in the middle of the month (15th or 16th).

Despite the fact that all letters of clarification are not binding, it is still worth listening to the opinion of the inspection authorities. Still in the same letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709, an example is given when in an organization, advance payment is set for the 25th day, and wages are paid on the 10th day of the next month. Formally, the requirements of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are observed, however, the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation cites a situation where a person starts work on the 1st of the month and he will receive an advance only on the 25th. The Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation considers this situation to be contrary to current labor legislation.
Naturally, if such a violation is discovered during an inspection, the employer can appeal the decision of state inspectors, in accordance with Art. 361 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, by submitting a corresponding application to the immediate supervisor of the inspector who drew up the protocol on the violation, to the chief state labor inspector of the Russian Federation, or in court. But it will be much calmer and cheaper if payments are made in accordance with the recommendations of control authorities.
For the employer, the main thing is not to forget to indicate in the relevant contracts or VTR rules the specific dates for the payment of the advance and salary. Indicating only the periods of their payments will be considered a violation. This requirement is enshrined in Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility for violation of advance payment rules
The obligation to make payments no less than twice a month is enshrined in Art. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, no one prohibits paying several advances per month, making three payments (every 10 days) or six payments (every 5 days).
If wages are paid only once a month, the organization making such payment violates current labor legislation, and its actions are qualified as an administrative offense.
In accordance with Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, for violation of labor legislation, the following fines are imposed:
- Officials– fine from 1 to 5 thousand rubles. If a person has already been prosecuted for a similar offense, then a fine of 10 to 20 thousand rubles, or disqualification from 1 to 3 years;
- Individual entrepreneurs– fine from 1 to 5 thousand rubles. If a person has already been prosecuted for a similar offense, then a fine of 10 to 20 thousand rubles;
- Legal entities– fine from 30 to 50 thousand rubles. If a legal entity has already been prosecuted for a similar offense, then a fine of 50 to 70 thousand rubles;
In addition, employees may demand compensation for delayed payment of wages, in accordance with Art. 235 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, since the situation of paying wages less than twice a month can be considered as untimely payment.
How to apply for a salary advance?
Depending on the method of issuing the advance (cash, transfer to a bank card, payment in kind), the list of documents that need to be completed will vary.

The general rule is that the advance payment must be issued using the same documents as the final payroll payment.
If an advance is issued:
- Cash: issuance is issued according to the statement of form T-53 or the cash receipt order KO-2. Since the advance is paid for an incomplete month, drawing up a statement in the T-49 form is not necessary. It is used to record deductions, accruals and payments for the whole month.
- Transfer to a bank card or account: the purpose of payment when paying an advance on wages should not be too long; a few symbols will suffice, for example: “Payroll for the 1st half of June 15.” In this case, it is necessary to make two entries: when transferring the advance - DEBIT 70 CREDIT 51 “monies were transferred for wages”, when transferring the bank commission - DEBIT 91-2 CREDIT 51 “commission retained by the bank.”
- In kind: based on the norms of Art. 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - a non-cash form of advance cannot be more than 20% of the total salary. It is necessary to make 5 entries: DEBIT 70 CREDIT 90-1 “revenue from the transfer of finished products to payroll”, DEBIT 90-2 CREDIT 43 (41) “writing off the cost of finished products”, DEBIT 90-3 CREDIT 68 SUBACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS” “VAT accrual”, DEBIT 90-9 CREDIT 99 “profit from the transfer of property for salary” or DEBIT 99 CREDIT 90-9 “loss from the transfer of property for salary”.
In accordance with Art. 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a loss resulting from the transfer of products or goods of own production reduces taxable profit in the usual manner.
Thus, it is quite difficult to clearly determine what percentage of the salary the advance will be in 2019. Logically, this payment should be from 20-50% depending on the form.
Taxes on salary advances
Due to the fact that the advance is a payment of part of the salary, no taxes or contributions are withheld from it, including personal income tax, contributions for medical, social, pension insurance, accidents and occupational diseases.
Personal income tax is withheld at the time of payment of income to the employee, after the advance payment of wages has been calculated. This moment is recognized as the last day of the month for which this income was accrued, or the last day of work of the employee (in case of dismissal). This is confirmed by letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, dated 08/09/2012 No. 03-04-06/8-232 and dated 05/26/2014 No. BS-4-11/10126, respectively.
Insurance premiums are calculated after all necessary payments have been made based on the results of the month, at the end of the month.
Contributions for accidents and occupational diseases are calculated from wages, and the advance is only part of it.
Additional materials on the topic:
Balance sheet 2019: Form 1, rules for filling out accounts, decoding the balance sheet by line Salary increase for public sector employees from January 1, 2019: latest news Payment of state fees to the court: posting state fees in accounting