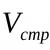The bank's financial assets include: Financial assets, financial liabilities and equity instruments: the essentials
The company's assets are divided into three groups: intangible, tangible and financial. Financial assets are a set of financial resources that belong to a company as property. These are the ones that will be discussed in this article.
The main task of finance. assets – the process of generating profit. Such assets are capable of generating income when used in operating or investment activities. This is their main feature.
This income is financial. assets are brought in as economic resources with a certain productivity. However, in the process of using such assets, some risks may arise.
Composition of financial assets
Financial assets include:
- Company money in cash and non-cash form;
- Various securities;
- Financial investments;
- Debts of debtors;
- Other settlement documents.
The bulk of financial assets in most firms consists of money and debts from debtors.
Let's look at the main types of financial assets in more detail.
Money
Cash is a medium of exchange. They evaluate all transactions performed. This asset can be expressed in both cash and non-cash form; both in domestic currency and in foreign currency.
Financial investments
Financial investments are a group of assets that have a documentary base confirming the company’s rights to own and use them.
This group of assets includes such sources of income as:
- Bank deposits;
- Providing interest-bearing loans to third-party companies;
- Third Party Securities;
- Securities of state and municipal nature;
- Contributions to the authorized capital of third-party companies.
Debts of debtors
Accounts receivable is the total amount of debts owed to the company by individuals. and legal persons in the position of debtors. This form of asset refers to all payments made to consumers. It can lead to the appearance of accounts payable.
Accounting for financial assets
When accounting for financial assets, they are divided into two groups:
- Production – their price may change due to the influence of external factors (exchange rates);
- Non-productive - their value is clearly defined and does not change in any case.
Here are the basic principles for accounting for such assets:
- Money is reflected in accounting at its nominal price. They can be taken into account in accounts 50 to 57.
- Securities and financial investments are reflected in account No. 58. If necessary, subaccounts can be opened for it.
- There are quite a few accounts for accounting for accounts receivable – from 60 to 76.
Financial market assets
The financial assets market has three directions:
- Credit market. He is the most in demand. Quite often, companies need to attract additional resources from outside.
- Valny market. Its existence is due to the need to service transactions made with foreign partners. The exchange of money is accompanied by changes in exchange rates.
- Stock market. It involves investing in financial assets - investing money and securities in projects that will generate profit in the future. Such a market is an integral part of the country's economy.
FINANCIAL ASSETS
FINANCIAL ASSETS
(financial assets) Money and rights (claims) to it, as distinguished from tangible (physical) assets such as land, buildings or equipment. Financial assets include money, securities that give the right to receive money, such as bills or bonds, and shares, which represent indirect ownership of the physical and financial assets of companies. Claims or rights relating to financial assets include domestic and foreign debt obligations of individuals, companies and governments. In addition, shares of financial institutions and various derivatives, such as options, are included in this category.
Economy. Dictionary. - M.: "INFRA-M", Publishing House "Ves Mir". J. Black. General editor: Doctor of Economics Osadchaya I.M.. 2000 .
Economic dictionary. 2000 .
See what "FINANCIAL ASSETS" is in other dictionaries:
Includes cash on hand; bank deposits; deposits; checks; insurance policies; investments in securities; obligations of other enterprises and organizations to pay funds for supplied products (commercial loan); portfolio investments in... ... Financial Dictionary
financial assets- Assets of an enterprise (company), which include (according to IFRS standards): cash; contractual rights to receive cash or other financial assets from another company; contractual rights to exchange... ... Technical Translator's Guide
Financial assets- (Financial assets) - assets of an enterprise (company), which include (according to IFRS standards): cash; contractual rights to receive cash or other financial assets from another company; conditioned... ... Economic and mathematical dictionary
This article lacks links to sources of information. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You can... Wikipedia
financial assets- Assets in the form of shares, bonds, rights, certificates, bank balances, etc., as opposed to tangible, physical assets. For example, real estate is a physical asset, shares in a mortgage investment trust (real estate... ... Financial and investment explanatory dictionary
Financial assets- (FINANCIAL ASSET) Assets that are: a) cash; b) a contractual right to receive cash or other financial assets from another company; c) the contractual right to exchange financial... ... Finance and stock exchange: dictionary of terms
Financial assets- include: funds stored in bank accounts and in the cash register of the enterprise; securities - shares, share certificates, bonds, certificates, payment orders, checks, bills, mortgages, etc., owned by the enterprise. Securities… … Commercial power generation. Dictionary-reference book
Financial assets- Claims (presentation of rights) to real estate... Investment Dictionary
Financial assets of the enterprise- see Enterprise assets... Encyclopedia of Law
Financial assets of the enterprise- see Enterprise assets... Large legal dictionary
Books
- , M. N. Mikhailenko. The concept of the financial system and its purpose are outlined. The characteristics of the functions of the financial system are given. The main elements of the financial system - financial institutions, as well as...
The concepts of “financial assets” and “financial liabilities” are found in the literature on personal finance management very often and these concepts are not interpreted unambiguously by different financial specialists.
The concept of financial ASSETS
In my School of Life materials, the concept of financial assets is used in the following sense:
- financial assets- This is property that can be converted into money.
Is real estate a financial asset or a financial liability?
It is believed that if real estate can be turned into money, then it is an asset. If real estate cannot be converted into money, then it is not an asset, but simply real estate.
In answer to the question asked, we can say that if you have real estate, but it is residential real estate and you live in it and are not going to sell it under any circumstances, then this real estate cannot be considered an asset.
If you can sell it if necessary, then it is undoubtedly an asset.
Financial assets may or may not generate income.
For example, if you rent out your property, then this property is a source of income for you. Sometimes in this case they say that a financial asset “ creates cash flow" But even if you don't rent it out, the property is still a financial asset.
A gold bar you buy will never generate income for you, but since you bought it with the intention of selling it at a higher price in the future, it is definitely a financial asset.
Financial assets may require money for their maintenance.
For example, you can rent a bank safe to store a gold bar. And real estate requires ongoing repairs, payment of utility bills, and so on.
Financial Asset Management
Considering the above, it makes sense to competently manage your financial assets and regularly evaluate how profitable it is to own a particular financial asset.
If the increase in the price of a financial asset and the income it generates do not cover the costs of its maintenance, then you should think about selling such an asset.
The concept of financial LIABILITIES
There is even more confusion with the concept of financial liabilities than with the financial concept of assets. In financial management, the concept of financial liabilities is the sources of financial resources used to create financial assets.
In subsequent materials from my School of Life, it is proposed to understand financial liabilities as sources of money that require repayment.
To put it simply, financial liabilities– these are our debts, for example, bank loans, loans, loans. The division of property into such financial concepts as assets and liabilities is very conditional.
At the same time, this division into financial assets and liabilities allows us to fairly objectively assess the degree of health of our financial relationships in managing personal finances.
Financial Assets and Liabilities Management
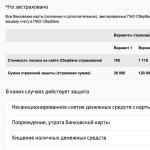
To understand whether you are in a normal position in managing your personal finances, make a table with a list of your financial assets according to their current valuation, that is, at the price for which they can actually be sold today, as well as a list of your financial liabilities (i.e. debts) ).
Financial Dependency Ratio (FDC)
KFZ = Financial liabilities (Debts) / Financial Assets.
If the Financial Dependence Ratio is less than one, that is KFZ< 1 , then you have normal personal finance management.
If the Financial Dependence Ratio exceeds one, that is KFZ > 1, then this shows that your personal finance management needs adjustment.
If the Financial Dependence Ratio exceeds two, that is KFZ > 2, then you have a pronounced “financial fever”, which can soon lead to very serious financial consequences.
However, if the Financial Dependency Ratio is less than 1, this does not mean that you can relax and not pay attention to managing your financial assets and liabilities. Many “financial diseases” develop for a long time without visible signs of illness.
How to manage financial assets so that they bring money
The simplest way to manage financial assets:
- is to acquire a financial asset that brings in money.
However, the acquisition of a profitable financial asset may require very significant financial investments.
Moreover, practice shows that the more reliable a financial asset is in terms of its ability to generate money, the more expensive this financial asset is worth.
The modern financial market provides ample opportunities for purchasing financial assets of different classes. If you decide to go this route, then you should start building enough capital to buy the financial assets that interest you.
There is another way to manage financial assets so that they bring in money.
You can create financial assets with your own hands, investing not only money, but also your own strength, time, talents and knowledge.
The more talented and energetic you are, the more time you can devote to creating your financial asset, the less money you will need and, accordingly, the financial return on investment will be greater.
The price of an income-generating financial asset is usually equivalent to the profit from owning this asset for 5-10 years.
Buying a financial asset at that price or spending several years creating such a financial asset on your own is one of the components of financial planning.
When you are employed, you create financial assets not for yourself, but for your employer.
If you want financial assets to appear in your personal life and for them to bring you money, you must get used to the idea that
- You should spend some part of your resources (money, time, effort, knowledge) not on entertainment and work for other people, but on creating your own financial assets.
Where to get extra resources to create your own financial assets
Every person has a lot of opportunities to create their own financial assets, you just need to look hard for them. For example, the average Russian spends 4.5 hours a day watching TV.
A financial asset is a fund representing financial liabilities and claims. Moreover, such funds allow the owner to have the right to receive one or more payments from some other institutional unit. The latter in this case acts as a debtor on the basis of an agreement that was previously recorded between them. Thus, a financial asset is a specific form of property relations. It is precisely this that provides the owner with the opportunity to make a profit. This concept characterizes all available enterprises
Components

Like any other item, an enterprise asset is a rather complex structure that consists of many components. Let us list the most significant of them. This concept traditionally includes cash, securities, deposits and deposits, cash on hand, shares and insurance policies. In addition, it should be noted that this article of accounting documentation also includes shares of the organization in question, as well as packages and investments in other companies. Accounting for financial assets should be carried out by specialists who do not forget that in addition to all of the above, the following items are also attributed to such an economic term: monetary gold, technical reserves, foreign investments, borrowings from the currency fund. When analyzing everything that was said earlier, we can conclude that all financial transactions belonging to this category consist of two main groups, which are called “asset for the creditor” and “liability for the debtor.”

Like any other product that can be found in a wide range of modern markets, the desired quantity has a sufficient number of characteristics and factors responsible for the feasibility of various operations associated with it. However, there are many distinctive features. The most obvious example is the following: a financial asset is not acquired for direct use. The purpose of their occurrence is considered to be investment in any part of the production process. If, as a result of such events, the asset contributed to the increase in profit, then it is considered that it was used rationally. In addition, it should be taken into account that the receipt of income must be regular and directly depend on the volume of the asset invested to obtain it.
Risk, return and price
Data is the most important asset. Risk is the likelihood that an entrepreneur will suffer losses as a result of his activities. Profitability is an interest rate calculated per year, which characterizes the amount of return on invested capital investments. The price, in turn, represents the valuation of the asset in monetary terms.
Financial assets (FA) are understood as the rights of an organization to income from the operation of real assets. Investment contributions to FA provide the institution with the opportunity to further profit from real resources acquired through investment.
Financial assets include the following categories:
- cash and non-cash funds;
- shares and other securities;
- accounts receivable;
- various financial investments;
- payment documents on the way, etc.
Valuation of financial assets is the determination of the amount of monetary resources into which FA can be converted. The assessment is carried out to monitor the current financial condition and level of solvency of the organization.
The assessment is carried out in several stages:
- Calculation of established and expected cash flows, analysis of the likelihood of the organization receiving certain material resources.
- Determining the appropriate interest rate to discount the flow.
- Calculation of the actual cost of FA.
Types of financial assets
The main types are equity and debt securities, as well as derivatives. The key purpose of their circulation is to generate profit for the organization.
FAs are grouped according to a number of characteristics and signs. Let's present their classification in the table:
| Classification feature | FA type |
|---|---|
| The nature of participation in the investment process |
|
| Investment period |
|
| Risk level |
|
| Accounting method |
|
| Liquidity level |
|
| Level and security of income |
|
| Purposes of acquisition and use |
|